Introduction To Sarf
Sarf (Morphology) is the Arabic science that assigns meanings to words through patterns and endings. We will demonstrate this with an example, but it's important to keep in mind that the concepts here are not intended to be memorized. This lesson is just to give you an idea of what Sarf is and how it is used.
The Arabic word اِسْتَنْصَرُوْا translates as, "They sought help". Notice how it required three English words to translate this one Arabic word. This will often be the case as Arabic words are structured to convey additional meanings via vowels, patterns and endings.
From this translation, we can infer seven unique meanings, each of which adds an additional layer of understanding. Before we jump into these, it's useful to know that Arabic words are typically based on three (sometimes four) root letters. We can apply certain conventions to these root letters to enhance the meaning.
Take the word "help" in English, which we can consider to be root letters. We can then apply the pattern of adding an "-ing" suffix to convey the additional meaning of present tense, or "-ed" for past tense, or "-s" to imply a continuous action.
If we change the root letters to "cook" and use the same rules, we get: cooking, cooked, and cooks. The meaning from the suffixes doesn't change, but the root meaning changes since we changed the root letters. The meaning of these root letters is what we would use a dictionary for, and the additional meanings from the patterns and endings wouldn't be found in a dictionary as they are standards of the language that we would be expected to know.
Now, let's analyse all seven of the meanings we can understand from the word اِسْتَنْصَرُوْا, "they sought help".
1. Help
The dictionary meaning of help comes from the three root letters ن ص ر. Arabic is predominantly a triliteral language, which means most words in the language can be traced back to three root letters, just like اِسْتَنْصَرُوْا and its three root letters ن ص ر.
As a result of this, often, Sarf rules change the vowels on these root letters or add prefixes/suffixes. We therefore often refer to these root letters as the ف letter, the ع letter, and the ل letter respectively, after the word فَعَلَ which is used as the token Sarf word to practice its rules. You will see this extensively, so don't worry too much if this is not 100% clear right now.

2. The Notion of Seeking
The additional meaning of "seeking" the action (help), comes from the addition of the ست suffix.

3. Past Tense
Arabic verbs that are in the present/future tense must start with one of four letters: أ ت ي ن which can be remembered using the word أَتَيْنَ. Since the verb does not start with one of these letters, we know it is in the past tense (they sought help vs they are seeking help).

4. Active Voice
The active voice (they sought help) vs the passive voice (help was sought by them) comes from a vowel pattern configuration.
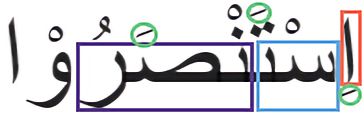
5. 6. 7. Gender, Plurality, and Person
The fact that a group of men (or men and women) are being spoken about (third person) comes from the Waw suffix. All three of these things are determined by the way a verb ends.
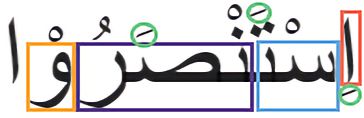
Final Takeaway
The purpose of this lesson was to introduce the science of Sarf. It was to demonstrate that out of the 7 meanings we understand from the word اِسْتَنْصَرُوْا, only one comes from the dictionary. The remaining 6 come from Sarf, where patterns, vowels, and endings convey the extra meanings.